Class06,07 Operators, Expressions
In Python, operators are special symbols that perform operations on variables and values. They are categorized based on their functionality: ⚙️
1. Arithmetic Operators ➕➖✖️➗
Used for mathematical operations:
+(Addition)-(Subtraction)*(Multiplication)/(Division → float)//(Floor Division → integer)%(Modulus → remainder)**(Exponentiation)
Python
print(5 + 3) # 8
print(10 // 3) # 3 (integer division)
print(2 ** 4) # 16 (2^4)
2. Assignment Operators ➡️
Assign values to variables (often combined with arithmetic):
=(Assign)+=(Add and assign)-=(Subtract and assign)*=(Multiply and assign)/=(Divide and assign)//=(Floor divide and assign)%=(Modulus and assign)**=(Exponentiate and assign)
Python
x = 5
x += 2 # Equivalent to x = x + 2 → 7
print(x) # Output: 7
3. Comparison Operators ⚖️
Compare values → return True or False:
==(Equal)!=(Not equal)>(Greater than)<(Less than)>=(Greater than or equal to)<=(Less than or equal to)
Python
print(5 == 5) # True
print(10 > 12) # False
4. Logical Operators 💡
Combine conditional statements:
and→Trueif both operands are trueor→Trueif at least one operand is truenot→ Inverts the result
Python
print((5 > 3) and (10 < 20)) # True
print(not (5 == 5)) # False
5. Identity Operators 🆔
Check if objects are the same in memory:
is→Trueif both variables point to the same objectis not→Trueif they are different objects
Python
a = [1, 2]
b = a
c = [1, 2]
print(a is b) # True (same object)
print(a is c) # False (different objects, even if same content)
6. Membership Operators 📍
Test if a value exists in a sequence (list, tuple, string, etc.):
in→Trueif value is foundnot in→Trueif value is missing
Python
fruits = ["apple", "banana"]
print("banana" in fruits) # True
print("grape" not in fruits) # True
7. Bitwise Operators 🧮
Operate on binary representations:
&(AND)|(OR)^(XOR)~(NOT)<<(Left shift)>>(Right shift)
Python
print(5 & 3) # 1 (binary: 101 & 011 = 001)
print(5 >> 1) # 2 (binary 101 shifted right → 10)
Operator Precedence 📏
Order of evaluation (highest to lowest):
- Parentheses
()괄호 - Exponentiation
**⬆️ - Bitwise shifts
<<,>>⬅️➡️ - Multiplication/Division
*,/,//,%✖️➗ - Addition/Subtraction
+,-➕➖ - Comparison
==,!=,>, etc. ⚖️ - Logical NOT
not✖️ - Logical AND
and🤝 - Logical OR
or➕
Example:
Python
result = 10 + 3 * 2 # 16 (3*2=6 → 10+6)
print(result) # Output: 16
Key Notes: 📌
- Type Compatibility: Operators may behave differently based on data types (e.g.,
+concatenates strings but adds numbers). 📊 - Chaining Comparisons: Python allows
a < b <= c. 🔗 - Short-Circuiting: Logical operators (
and/or) stop evaluating once the result is determined. ⚡
Expressions in Python
An expression is a combination of values, variables, operators, and function calls that Python evaluates to produce a single value. Expressions can be as simple as a single variable or as complex as a multi-operation calculation.
Key Characteristics of Expressions:
- Always evaluate to a value (e.g.,
5 + 3→8) - Can contain operators, literals, variables, and function calls
- Can be part of larger statements (e.g., inside
ifconditions, assignments)
Arithmetic Expression Examples
| Example | Evaluation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
5 + 3 * 2 | 11 | Multiplication before addition |
(5 + 3) * 2 | 16 | Parentheses change order |
10 / 3 | 3.333... | Regular division (float result) |
10 // 3 | 3 | Floor division (integer result) |
10 % 3 | 1 | Modulus (remainder) |
2 ** 4 | 16 | Exponentiation (2⁴) |
-5 + 8 | 3 | Unary negative + addition |
3.5 * (2 + 1) | 10.5 | Mixed float/integer operations |
(2 + 3j) * (1 - 1j) | (5+1j) | Complex number arithmetic |
Expression Types with Examples
1. Simple Arithmetic
python
x = 5 y = 3 result = x * y - 2 # Evaluates to 13 (5*3=15 → 15-2)
2. With Functions
python
import math
hypotenuse = math.sqrt(3**2 + 4**2) # √(9+16) = 5.0
1. Area of a Triangle
Area = 0.5 × base × height
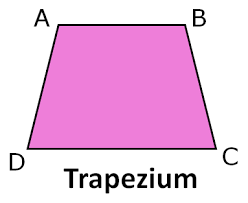
2. Area of a Trapezium
Area = 0.5 × (a + b) × height
(where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides)
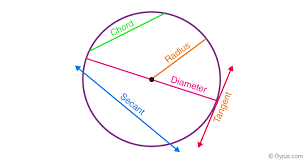
3. Area of a Circle
Area = π × radius²
(π ≈ 3.14159)
4. Kilometers to Miles
Miles = Kilometers × 0.621371
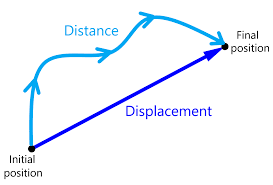
5. Displacement (Physics)
s = u×t + ½×a×t²
(where u = initial velocity, t = time, a = acceleration)
6. Surface Area of a Cuboid
Surface Area = 2 × (lw + wh + hl)
(where l = length, w = width, h = height)
More Area/Volume/Surface Area Calculations:
- Area of a Rectangle/Square: Simple and fundamental.
- Area of a Parallelogram: Similar to a rectangle but with an angle consideration.
- Area of a Rhombus: Can be calculated using diagonals.
- Volume of a Cube: Straightforward.
- Volume of a Cuboid: Extension of a cube.
- Volume of a Cylinder: Involves pi and radius/height.
- Volume of a Cone: Related to a cylinder but with a factor of 1/3.
- Volume of a Sphere: Involves pi and radius cubed.
- Surface Area of a Cylinder: Two circles and a rectangle.
- Surface Area of a Cone: Base circle and a lateral surface.
- Surface Area of a Sphere: Simple formula involving pi and radius squared.
- Perimeter of a Rectangle/Square: Basic perimeter calculation.
- Circumference of a Circle: Directly related to the area of a circle.
- Area of a Sector of a Circle: A fraction of the circle’s area.
Conversions:
- Miles to Kilometers: Reverse of your existing program.
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: Common temperature conversion.
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: Reverse of the above.
- Pounds to Kilograms: Weight conversion.
- Kilograms to Pounds: Reverse of the above.
- Liters to Gallons: Volume conversion.
- Gallons to Liters: Reverse of the above.
- Meters to Feet: Length conversion.
- Feet to Meters: Reverse of the above.
- Hours to Minutes/Seconds: Time unit conversions.
Physics/Math Formulas:
- Calculate Velocity: Velocity=Displacement/Time
- Calculate Acceleration: Acceleration=ChangeinVelocity/Time
- Calculate Force: Force=Mass×Acceleration (Newton’s Second Law)
- Calculate Work Done: Work=Force×Distance
- Simple Interest Calculation: SimpleInterest=(Principal×Rate×Time)/100
- Compound Interest Calculation: More complex, involves exponents.
- Quadratic Equation Solver: Finds roots of a quadratic equation.
- Pythagorean Theorem: a2+b2=c2 (calculating hypotenuse or a side of a right triangle).
- Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator: Based on height and weight.
- Ohm’s Law: Voltage=Current×Resistance (or variations to find current/resistance).
